Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique used in the treatment of sports medicine injuries. It involves the use of a fiber-optic camera, which we place into a joint through a small incision in order to visualize ligaments, cartilage, and soft tissue. Through another small incision, we can then use small instruments to remove or repair broken or damaged tissue.
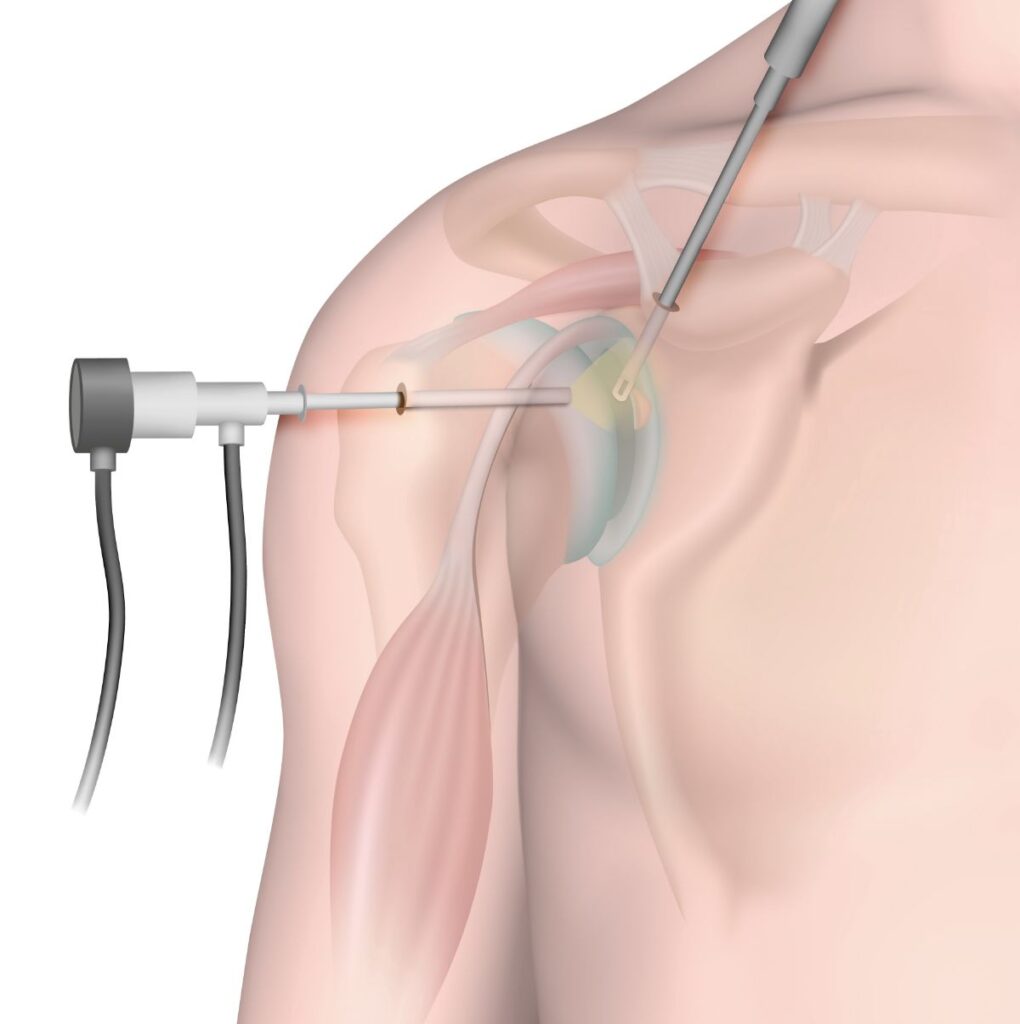
Shoulder Arthroscopy
Shoulder arthroscopy with rotator cuff repair is the term used to describe surgery performed for patients with a torn or damaged rotator cuff. The rotator cuff is comprised of four muscles that allow us to raise our arms up and perform overhead activities. The two rotator cuff muscles located on the top of the shoulder are the ones most commonly torn. In some patients, the space in the shoulder below the clavicle (subacromial space) is narrowed, which causes the rotator cuff to be pinched or impinged on with overhead motion. This can cause chronic tendonitis of the rotator cuff and lead to tearing of the rotator cuff muscles. Rotator cuff tears can also occur as a result of trauma—for example, falling on your shoulder or lifting a heavy object. Regardless of cause, a rotator cuff tear is a significant source of pain. Patients often develop difficulty with reaching overhead, pushing, pulling, or lifting items because of the pain associated with a rotator cuff tear. Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair is often done in conjunction with an arthroscopic subacromial decompression and distal clavicle excision for treatment of shoulder impingement accompanying a rotator cuff tear.






