5 minute read
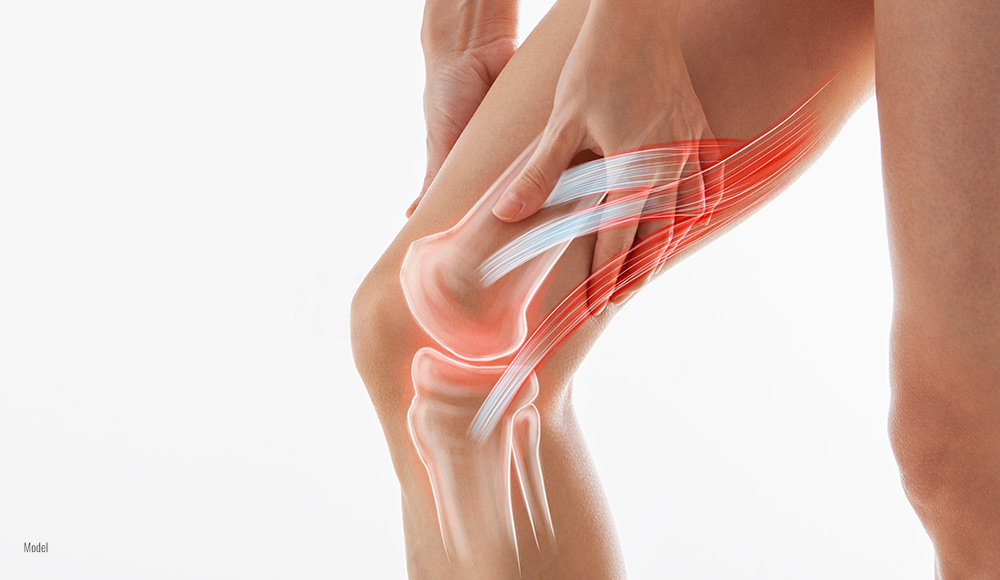
Osteoarthritis is a common form of arthritis that causes joint pain and stiffness, which worsens over time. Pain medications and physical therapy can be options for treating osteoarthritis. However, if these methods are insufficient in reducing pain and improving your range of motion, then some form of joint replacement surgery may be necessary. This blog discusses osteoarthritis and the non-surgical and surgical treatment options.
Dealing With Joint Pain
Whether you’re an athlete used to physically intense activities or live a less active lifestyle filled with common daily movements, your joints support you throughout your everyday life. Running, walking, bending, and lifting objects are just some of the movements your body may experience regularly, and your joints are responsible for carrying out these motions.
When there is continuous pain in your joints, it becomes difficult to perform everyday activities and do the things you want. Many people who experience joint pain find that they cannot do the activities they enjoy doing and struggle to perform necessary tasks. Joint pain can even make standing or sitting painful.
Since joint pain can be debilitating, people often seek treatment so that they can go back to their normal routines. However, some people are wary of surgical procedures and may think that surgery is their only treatment option. This is not the case. Experienced board-certified surgeons like Dr. Jason Snibbe perform joint replacement surgery only if it is absolutely necessary and will try alternative non-surgical methods before resorting to surgery.
What Is Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is known as the most common type of arthritis. An estimated 33 million adults in the United States have osteoarthritis. This chronic condition happens when the protective cartilage that surrounds the joints breaks down. Once the cartilage wears down, the underlying tendons and ligaments are forced to stretch, creating pain sensations. When the cartilage continues to diminish, there’s a risk of the bones rubbing against each other, causing more pain. Osteoarthritis can affect any joint, though it most often occurs in the hips, knees, and spine due to how these joints support the body’s weight.
As a degenerative disease, osteoarthritis typically worsens as the joints continue to deteriorate. Once damage occurs to the joints, it cannot be reversed. Many osteoarthritis treatments aim to manage pain symptoms and improve joint function.
What Are the Non-surgical Treatment Methods for Osteoarthritis?
Before deciding to go through with joint replacement surgery, it is essential to evaluate how your joint pain is affecting you. The following questions can be a good starting point to guide you through your decision:
- How often do you feel joint pain?
- Does your pain prevent you from doing activities you want? How often does this occur?
- Are you unable to perform everyday functions due to pain?
One of the best ways to determine which osteoarthritis treatment is right for you is to have a consultation with a board-certified orthopedic surgeon. When Dr. Snibbe meets new patients, non-surgical methods are usually tried first so surgical procedures can be avoided if possible.
Pain Medication
The first non-surgical approach that is typically tried is non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Examples of NSAIDs include ibuprofen, naproxen, aspirin, etc. These medications are meant to target the inflamed joint and relieve pain.
Physical Therapy
For some patients, physical therapy can be beneficial for improving their range of motion. Stretching exercises are commonly used in physical therapy for patients with joint pain to manage pain and prevent the joint disease from getting worse.
Alternative Methods
Depending on the patient and where the joint pain is located, alternative non-surgical treatments may be an option. Patients with osteoarthritis in their knees may benefit from wearing a knee brace. Icing the joint may provide pain relief for some patients. Additionally, steroid injections can also be used to manage pain.
What Is Robotic Assisted Surgery?
Dr. Snibbe performs robotic-assisted surgery in Los Angeles, CA, to relieve shoulder, hip, and knee pain in patients. Robotic-assisted surgery means the surgeon uses a robotic device to help them perform the procedure. Dr. Snibbe uses robotic technology to perform joint replacements on the shoulders, hips, and knees. Utilizing robotic technology allows surgeons to increase precision during the surgery, minimize complications, and result in a shorter recovery period.
What Are the Surgical Treatment Options for Osteoarthritis?
If non-surgical methods are not enough to relieve pain and improve the patient’s range of motion, and if the osteoarthritis is more advanced, then surgery may be the best option. Joint replacement surgeries utilize prosthetic implants to replace the damaged joint, relieving the patient of pain and helping them regain control of their movements. When joint replacements are performed with the assistance of robotic devices, the implants can be placed with advanced precision, allowing for the best possible results.
Want to Know More About Osteoarthritis Treatment and Robotic Assisted Surgery in Los Angeles, CA?
If joint pain has been affecting your everyday life and preventing you from participating in the activities you want, it may be time to consider osteoarthritis treatment. To learn more about treatment options, you can contact Dr. Snibbe’s office for more details. If you’re ready to begin treatment, scheduling a consultation with Dr. Snibbe can be one of the first steps in your pain relief journey.
During a consultation, you will discuss your medical history and pain symptoms and undergo an examination by Dr. Snibbe. You will learn more about your treatment options and whether you may be a good candidate for joint replacement surgery. If you choose to proceed with osteoarthritis treatment, a customized plan will be created for you.
To learn more about osteoarthritis treatment or to schedule your consultation in Los Angeles, CA, call Dr. Snibbe’s office at (310) 860-3048 or fill out our online contact form.






