Osteoarthritis (OA) of the Shoulder
Osteoarthritis of the shoulder is the loss of cartilage that covers the ball and socket of the joint.
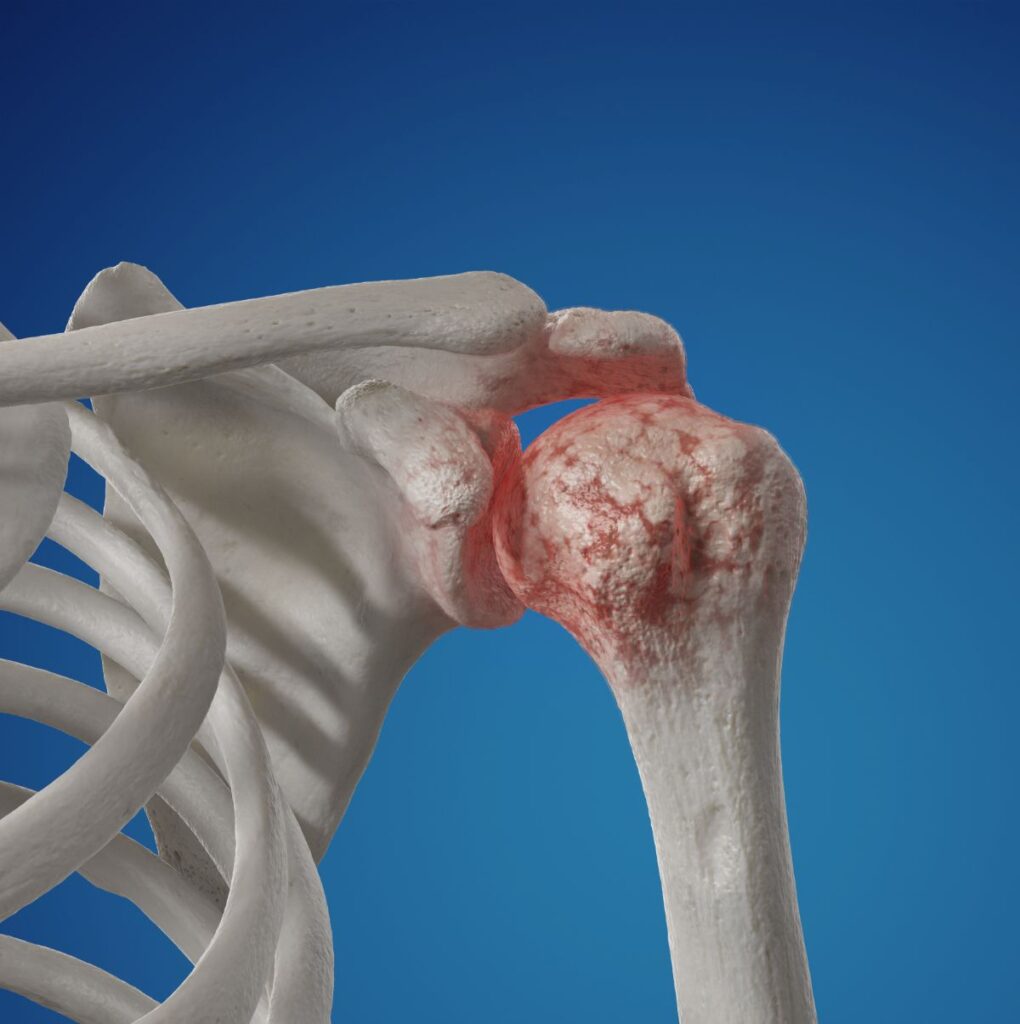
OA of the Shoulder
It commonly affects patients over 50 and includes complaints of stiffness, decreased range of motion, and pain in the shoulder, arm, upper back, and neck. Patients also present with difficulty raising the arm, lifting items, overhead activities, repetitive use of the arm, and usually an aching pain at night.
Initial evaluation of an arthritic shoulder consists of an X-ray in the office to evaluate the extent of cartilage loss and an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) to evaluate the condition of the rotator cuff.
Initial treatment consists of NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatories, such as ibuprofen, Advil, Aleve, etc.) and application of heat and/or ice to relieve the pain and inflammation in the shoulder joint. If loss of motion has occurred, stretching exercises or physical therapy is recommended to maintain one’s range of motion. Steroid injections are often provided for symptomatic relief.
If the osteoarthritis is advanced, total shoulder replacement surgery is considered. If a patient has a long history of rotator cuff injury, a reverse total shoulder replacement may be necessary.






